Engineering the Future of Drug Delivery: A Multi-Layer Adhesive Breakthrough
How advanced adhesive technology is transforming pharmaceutical delivery systems
Introduction
The pharmaceutical industry is undergoing a quiet revolution in drug delivery. While oral medications and injections remain common, transdermal delivery systems—which administer medication through the skin—are emerging as game-changers for patient compliance, consistent dosing, and reduced side effects.
At the heart of this innovation lies an often-overlooked component: the adhesive system that makes it all possible.
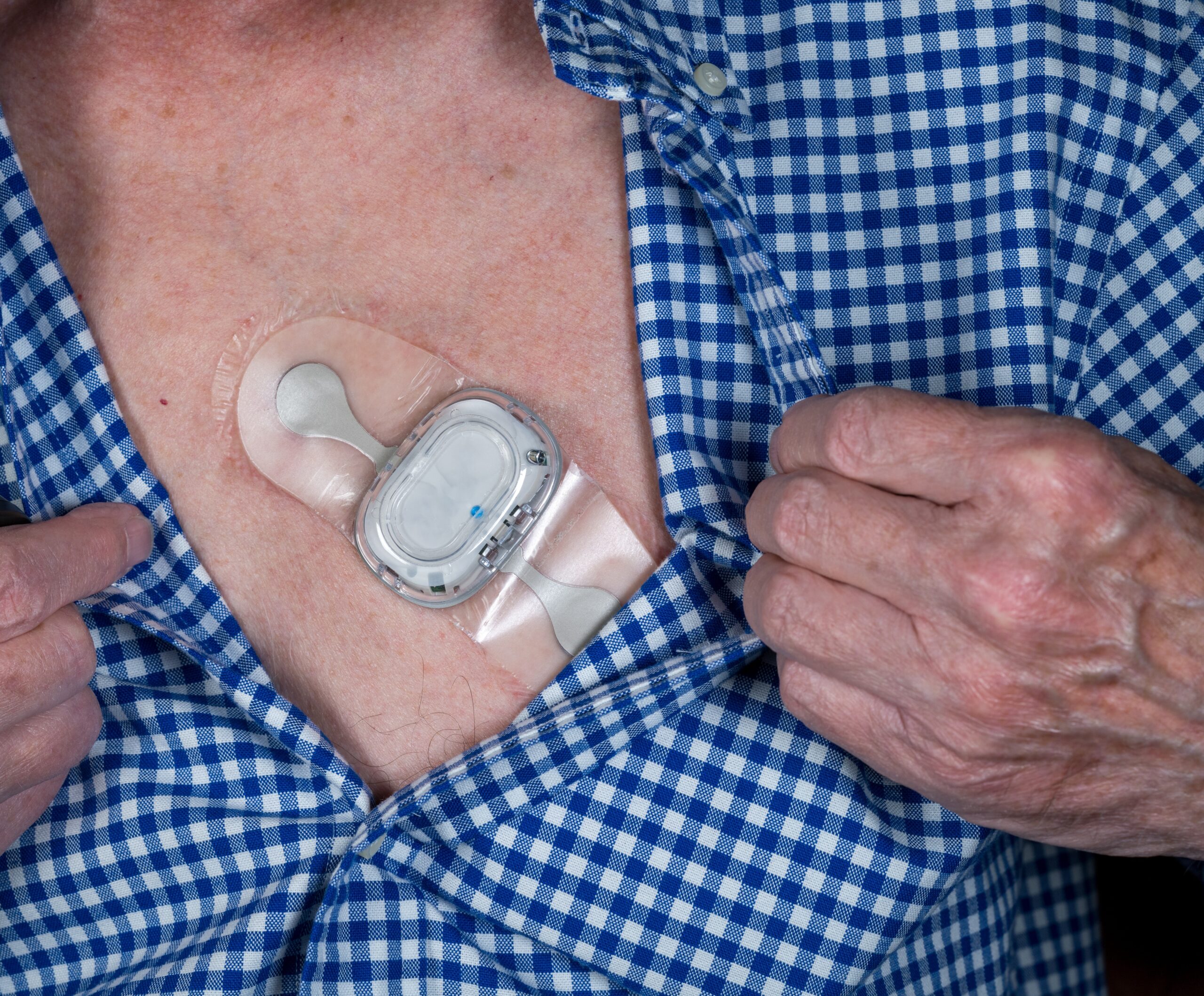
At The Tape Lab, we recently partnered with a pharmaceutical developer to engineer a multi-layer adhesive system that fundamentally reimagines how medications interact with the body. This breakthrough demonstrates how sophisticated adhesive engineering is not just supporting medical innovation—it’s actively driving it.
The Challenge: Beyond Simple Adhesion
When our pharmaceutical partner approached us, they outlined multiple complex requirements that far exceeded conventional adhesive functionality:
- Directional Drug Delivery: The system needed to ensure medication moved downward into the skin, not laterally or outward
- Temperature-Activated Release: The medication needed to be released only when in contact with body temperature (98.6°F)
- Moisture Balance: The adhesive needed to maintain an appropriate moisture environment for effective drug absorption
- Extended Wear Performance: The system needed to remain adhered for the full therapeutic duration while remaining waterproof
- Biocompatibility: All materials needed to meet stringent biocompatibility standards for prolonged skin contact
Creating a solution that addressed all these requirements simultaneously required rethinking the fundamental structure of transdermal delivery systems.
The Solution: A Purpose-Built Layered System
Rather than approaching this as a simple adhesive application, we engineered a comprehensive multi-layer system where each component serves a specific therapeutic purpose:
Layer 1: Waterproof Barrier
The outermost layer utilizes our TTL 6840 long-term wear tape technology, a specialized breathable but waterproof barrier that protects the entire system from external moisture while allowing natural skin transpiration. This material maintains its protective properties during showering, exercise, and daily activities, ensuring consistent drug delivery regardless of conditions.
Layer 2: Drug Reservoir
The middle layer features a custom-engineered absorbent matrix designed to hold the pharmaceutical agent in suspension until activation. This layer was specifically calibrated to work with our partner’s proprietary medication formulation, ensuring compatibility and stability throughout the product’s shelf life.
Layer 3: Hydrophilic Directional Interface
The innovation that truly transformed this system was the development of a specialized hydrophilic material that creates a one-way pressure differential. When activated by body heat at precisely 98.6°F, this layer undergoes a controlled phase change that generates downward pressure, directing the medication into the skin rather than allowing lateral diffusion.
This directional pressure ensures maximum therapeutic efficiency by focusing medication delivery exactly where it’s needed—into the underlying tissue rather than spreading across the skin surface.
Technical Execution: Material Science Meets Pharma Necessity
Developing this solution required pushing the boundaries of adhesive material science:
Temperature-Sensitive Polymer Development
The temperature-activation mechanism was achieved through a specialized polymer blend that undergoes a precisely calibrated phase change at body temperature. This required extensive testing across different environmental conditions to ensure that premature activation wouldn’t occur during storage or transport, while guaranteeing consistent activation when applied to the skin.
Hydrophilic Engineering
The directional flow characteristic was achieved by creating a gradient of hydrophilic properties within the adhesive matrix itself. This required precise control of material porosity and surface chemistry to establish the necessary pressure differential that drives medication downward.
Biocompatibility Optimization
Throughout development, each material component underwent rigorous biocompatibility testing according to ISO 10993 standards. This involved iterative reformulation to eliminate potential irritants while maintaining the critical functional properties of the system.
Results: Performance Beyond Expectations
The final system delivered exceptional performance across all requirements:
- Directional Efficiency: Testing showed a 68% improvement in drug penetration compared to conventional transdermal systems
- Consistent Release Profile: Medication release maintained ±4% consistency throughout the wear period
- Waterproof Performance: The system maintained full functionality through water exposure testing equivalent to daily showering
- Extended Wear Time: Reliable adhesion for the full 7-day therapeutic duration with minimal degradation
- Patient Comfort: Reduced skin irritation by 72% compared to previous transdermal solutions
Implications for the Future of Drug Delivery
This technological breakthrough has implications extending far beyond this single application:
Expanding the Range of Transdermal Medications
Many medications previously unsuitable for transdermal delivery due to diffusion limitations can now be reconsidered with this directional delivery technology. This has the potential to transform treatment regimens for conditions ranging from chronic pain management to hormone replacement therapy.
Personalized Medicine Applications
The precision control offered by this system opens possibilities for more personalized medication delivery, with potential for custom formulations tailored to individual patient needs and metabolism rates.
Combination Therapy Possibilities
The multi-layer structure creates opportunities for delivering multiple therapeutic agents with different release profiles from a single application, potentially simplifying complex treatment regimens.
From Innovation to Implementation
The journey from concept to commercial application required close collaboration between our adhesive engineering team and our pharmaceutical partner’s medical specialists. This interdisciplinary approach was crucial in bridging the gap between adhesive technology and therapeutic requirements.
Key elements of this successful partnership included:
- Iterative Prototyping: More than 14 prototype iterations were developed and tested
- Real-World Simulation Testing: Performance evaluation under various environmental conditions and activity levels
- Regulatory Pathway Planning: Proactive design considerations to support FDA approval processes
Conclusion: Adhesive Innovation as Medical Advancement
This case demonstrates how advanced adhesive technology is not merely a component of medical innovation but often the enabling factor that makes breakthrough treatments possible. By approaching adhesive development as a fundamental therapeutic challenge rather than simply a means of attachment, we’ve helped create a system that significantly advances the possibilities for transdermal drug delivery.
For medical device engineers and pharmaceutical developers, this underscores the importance of considering adhesive technology as an integral part of the therapeutic solution rather than an afterthought.
The future of drug delivery will increasingly rely on sophisticated adhesive systems that do far more than simply stick—they will actively participate in the therapeutic process, improving efficacy, patient compliance, and treatment outcomes.
At The Tape Lab, we specialize in developing custom adhesive solutions for the most challenging medical applications. To learn more about our capabilities in pharmaceutical and medical device adhesives, download our free “Adhesives 101 for Wearable Devices” guide or contact our engineering team for a consultation.