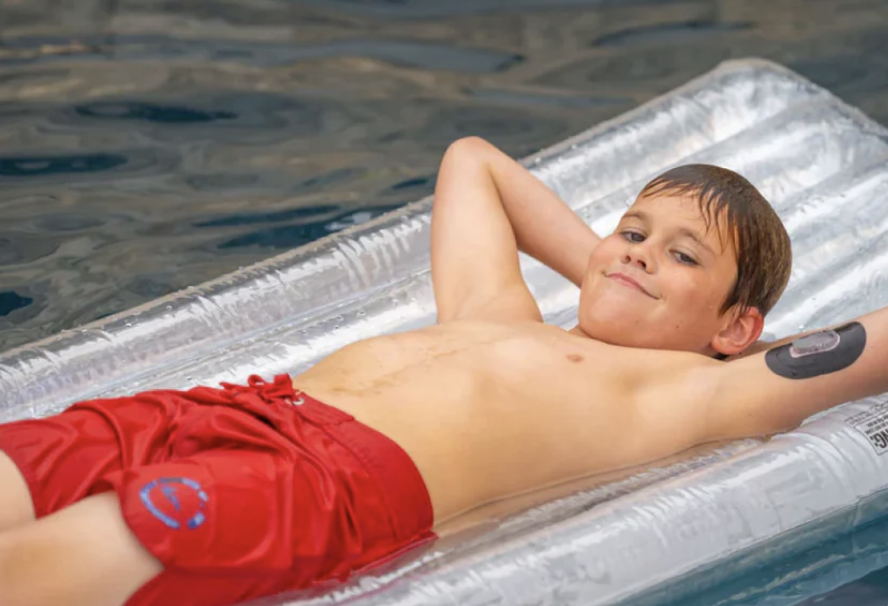
In many applications across industries, from medical to automotive, and even in everyday household tasks, the ability to adhere materials reliably in wet or submerged conditions is crucial. Waterproof adhesives play a significant role in ensuring that bonds remain intact despite exposure to moisture, water, or other liquids.
While waterproof adhesives are indispensable in various fields, their role in the medical industry is particularly critical due to the unique demands of medical applications. In a sector where hygiene, safety, and reliability are paramount, waterproof adhesives provide essential solutions for ensuring that medical devices and components perform optimally even in the presence of moisture or bodily fluids. The evolution of medical adhesives has also been marked by significant advancements in materials and technology, leading to increasingly sophisticated formulations that offer enhanced biocompatibility , durability, and resistance to bodily fluids, thereby improving the safety and effectiveness of medical devices and applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the types of waterproof adhesives used in medical applications, their benefits, and their diverse uses across the healthcare landscape.
Waterproof Adhesives in Medical Applications
Waterproof adhesives are specifically formulated to maintain their adhesive properties despite exposure to moisture. In medical settings, these adhesives are crucial for a variety of reasons. They ensure that medical devices and equipment remain securely attached and function effectively even when exposed to bodily fluids or cleaned with disinfectants. They are also essential in applications that require durability and reliability, such as wound care, device assembly, and surgical procedures.
The demand for waterproof adhesives in the medical field is driven by the need for products that can endure rigorous cleaning protocols, resist degradation from exposure to bodily fluids, and provide consistent performance under diverse conditions. Medical-grade waterproof adhesives must comply with stringent regulatory standards and undergo rigorous testing to ensure they are safe for use in healthcare environments.
Types of Waterproof Adhesives Used in Medical Applications
Various types of waterproof adhesives are employed in medical applications, each offering specific properties suited to different needs. Here are the main types:
1. Medical-Grade Waterproof Silicone Adhesives
Medical-grade silicone adhesives are widely used in medical applications due to their excellent flexibility, biocompatibility, and resistance to moisture and temperature extremes.
- Characteristics: Silicone adhesives provide a strong, flexible bond that can accommodate the movement of tissues and materials. They are also resistant to water, UV light, and temperature fluctuations, making them suitable for long-term applications.
- Applications: Commonly used for bonding medical devices, sealing wound dressings, and attaching electrodes in diagnostic and therapeutic devices. Their flexibility and water resistance make them ideal for applications that involve direct contact with the skin or bodily fluids.
2. Medical-Grade Waterproof Acrylic Adhesives
Medical-grade acrylic adhesives offer strong bonding capabilities and excellent resistance to water and various environmental conditions.
- Characteristics: Acrylic adhesives are known for their high bond strength, clarity, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. They also cure quickly and provide a durable bond.
- Applications: Often used in the assembly of medical devices, including packaging and labeling. They are also used for adhesive strips and wound closure products due to their strong adhesion and resistance to moisture.
3. Waterproof Epoxy Adhesives
Epoxy adhesives are used in medical applications for their high strength and durability.
- Characteristics: Epoxy adhesives consist of a resin and a hardener that form a strong, rigid bond when cured. They offer excellent water resistance and can withstand exposure to various fluids and chemicals.
- Applications: Used for bonding components of medical devices, such as prosthetics and surgical instruments. Epoxies are also used in manufacturing processes where a strong, permanent bond is required.
4. Waterproof Polyurethane Adhesives
Polyurethane adhesives are versatile and offer strong adhesion and flexibility.
- Characteristics: Polyurethane adhesives provide a flexible, durable bond and are resistant to water, chemicals, and temperature changes. They are also known for their ability to bond to a wide range of materials.
- Applications: Used in medical device assembly, including the bonding of components in durable medical equipment and orthopedic devices. Their flexibility and strength make them suitable for applications requiring resilience under stress.
Key Benefits of Medical Waterproof Adhesives
Waterproof adhesives offer several critical benefits in medical applications, ensuring that devices and products meet high standards of safety, performance, and reliability.
1. Enhanced Durability
Waterproof adhesives are designed to maintain their bonding strength even in challenging environments. This durability is essential in medical applications where devices and products are often exposed to bodily fluids, cleaning agents, and environmental factors that can affect adhesion.
2. Improved Safety
In medical settings, ensuring that adhesives do not cause adverse reactions is crucial. Waterproof adhesives used in medical applications are typically biocompatible and tested to ensure they do not cause irritation or other negative effects when in contact with skin or tissues. This enhances patient safety and ensures that devices function as intended.
3. Reliable Performance
Waterproof adhesives provide consistent performance in various conditions, including high humidity, exposure to fluids, and temperature fluctuations. This reliability is vital for medical devices that need to perform consistently over time and in different environments.
4. Ease of Use
Many waterproof adhesives are designed for ease of application, with features such as quick curing times and user-friendly formulations. This ease of use simplifies the manufacturing process and ensures that medical devices can be assembled efficiently without compromising quality.
Applications of Waterproof Adhesives in Medical Settings
Waterproof adhesives are used in a wide range of medical applications, each requiring specific properties to ensure optimal performance and safety. Here are some notable applications:
1. Wound Care and Dressings
Waterproof adhesives are essential in wound care products, such as waterproof adhesive bandages and dressings. These adhesives help secure the dressing in place while protecting the wound from moisture and contaminants. They also ensure that the dressing adheres to the skin without causing irritation or discomfort.
2. Medical Device Assembly
In the assembly of medical devices, waterproof adhesives are used to bond components securely. This includes devices such as insulin pumps, diagnostic equipment, and surgical instruments. The adhesive must provide a strong, durable bond while resisting exposure to fluids and cleaning agents.
Specifically, waterproof adhesives play a pivotal role in the effectiveness and comfort of wearable medical devices by ensuring they adhere securely to the skin despite exposure to moisture, sweat, and environmental conditions. These adhesives, such as medical-grade silicones and specialized acrylics, are formulated to provide a durable, flexible bond that conforms to the body’s contours, allowing for uninterrupted wear and accurate performance of the device. By resisting degradation from bodily fluids and maintaining their adhesive properties under varying conditions, waterproof adhesives help ensure that devices like glucose monitors and heart rate sensors remain reliably attached, thus supporting continuous health monitoring and enhancing user experience. Their development is crucial for advancing wearable technology, contributing to both the longevity and efficacy of these vital health management tools.
3. Catheters and Tubing
Catheters and tubing used in medical procedures often require waterproof adhesives to ensure secure connections and prevent leaks. The adhesives used in these applications must be biocompatible and capable of withstanding exposure to bodily fluids.
4. Prosthetics and Orthotics
Prosthetic limbs and orthopedic devices rely on waterproof adhesives for bonding components and attaching cushioning materials. These adhesives must provide a strong bond while allowing for flexibility and comfort.
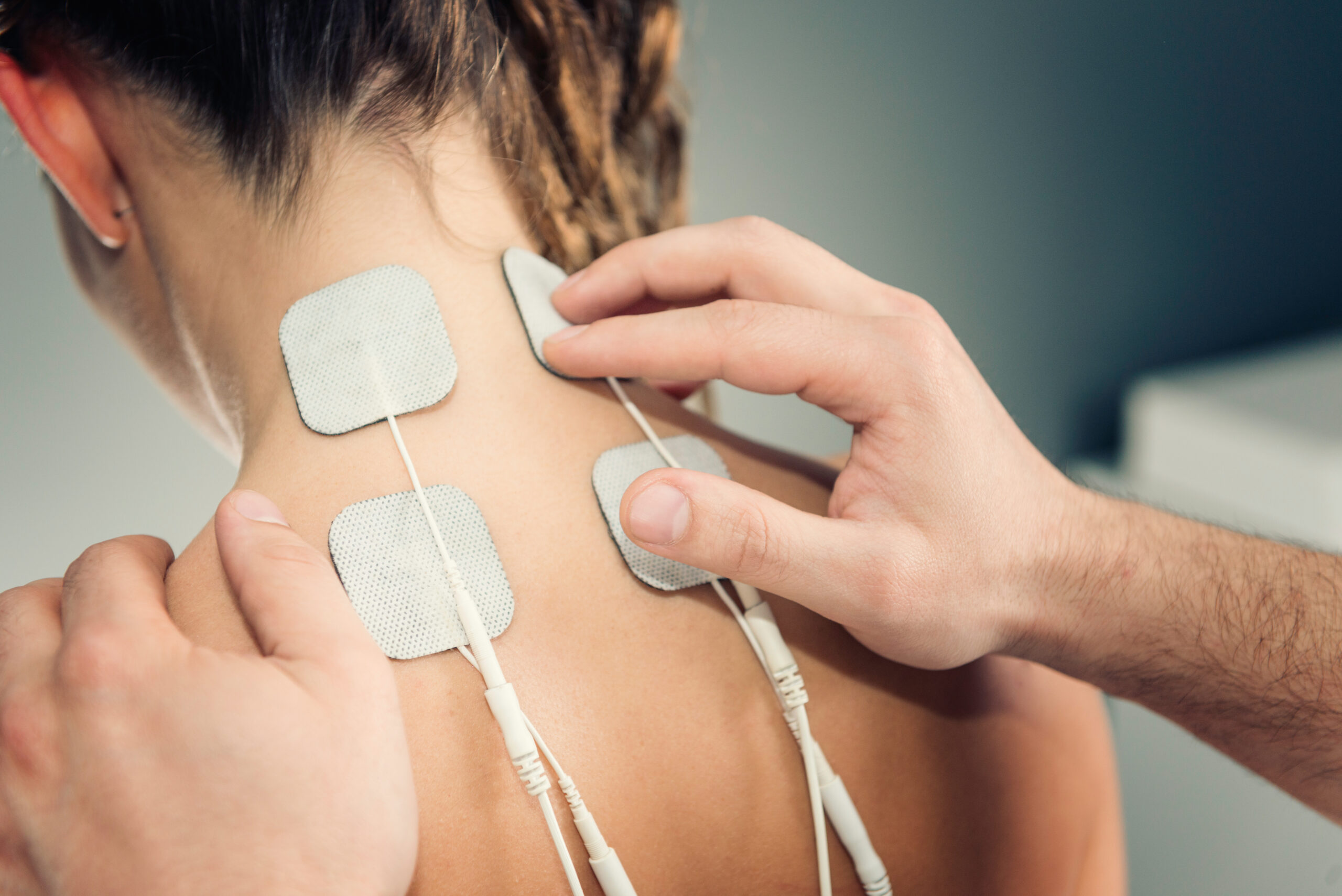
5. Electrodes and Sensors
Waterproof adhesives are used to attach electrodes and sensors to the skin or other surfaces in diagnostic and therapeutic devices. The adhesive must ensure a secure attachment while remaining effective in the presence of sweat and other bodily fluids.
6. Medical Packaging
In medical packaging, waterproof adhesives are used to seal packages and ensure they remain sterile. This includes packaging for sterile medical instruments, pharmaceuticals, and other healthcare products.
Regulatory Considerations for Medical-Grade Waterproof Adhesives
In the medical industry, waterproof adhesives must adhere to strict regulatory standards to ensure their safety and efficacy. Key regulatory considerations include:
1. Biocompatibility Testing
Waterproof adhesives used in medical applications must undergo rigorous biocompatibility testing to ensure they do not cause adverse reactions when in contact with tissues or bodily fluids. This testing typically includes evaluations for cytotoxicity, sensitization, and irritation.
2. Sterilization Compatibility
For adhesives used in the packaging of sterile medical products, they must be compatible with sterilization processes, such as autoclaving or radiation. The adhesive should not degrade or affect the sterility of the package.
3. Compliance with Standards
Medical-grade adhesives must comply with various international standards and regulations, such as ISO 10993 for biocompatibility and FDA regulations for medical devices. Compliance ensures that the adhesive meets quality and safety requirements.
Best Practices for Using Waterproof Adhesives
To achieve the best results with waterproof adhesives in medical applications, consider the following best practices:
1. Select the Right Adhesive
Choose an adhesive that meets the specific requirements of the application, including biocompatibility, water resistance, and flexibility. Consider factors such as the materials being bonded, environmental conditions, and regulatory requirements.
2. Ensure Proper Surface Preparation
Proper surface preparation is essential for achieving a strong bond. Ensure that surfaces are clean, dry, and free from contaminants before applying the adhesive. This helps ensure optimal adhesion and performance.
3. Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions
Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for application, curing times, and storage conditions. Different adhesives have specific requirements that must be followed to achieve the best results.
4. Test Adhesive Performance
If possible, conduct performance testing to verify that the adhesive meets the required standards for the application. This helps ensure that the adhesive provides the desired bond strength and durability.
5. Monitor and Maintain Quality
Regularly monitor the performance of medical devices and products that use waterproof adhesives. Implement quality control measures to ensure that the adhesive maintains its effectiveness and does not degrade over time.
Get Custom Waterproof Adhesives Created for Your Medical Product
At The Tape Lab, we’re not just manufacturing adhesives and other flexible medical materials; we’re crafting partnerships to bring your custom innovations to life. We specialize in customizing, designing, and manufacturing innovative adhesive tape and flexible materials into engineered products that best meet your needs. Let’s combine your vision with our knowledge and industry-leading capabilities to create a custom adhesive solution.
Already have an idea of what you need? Request a Quick Quote
Want to pick the brain of an expert? Contact The Tape Lab