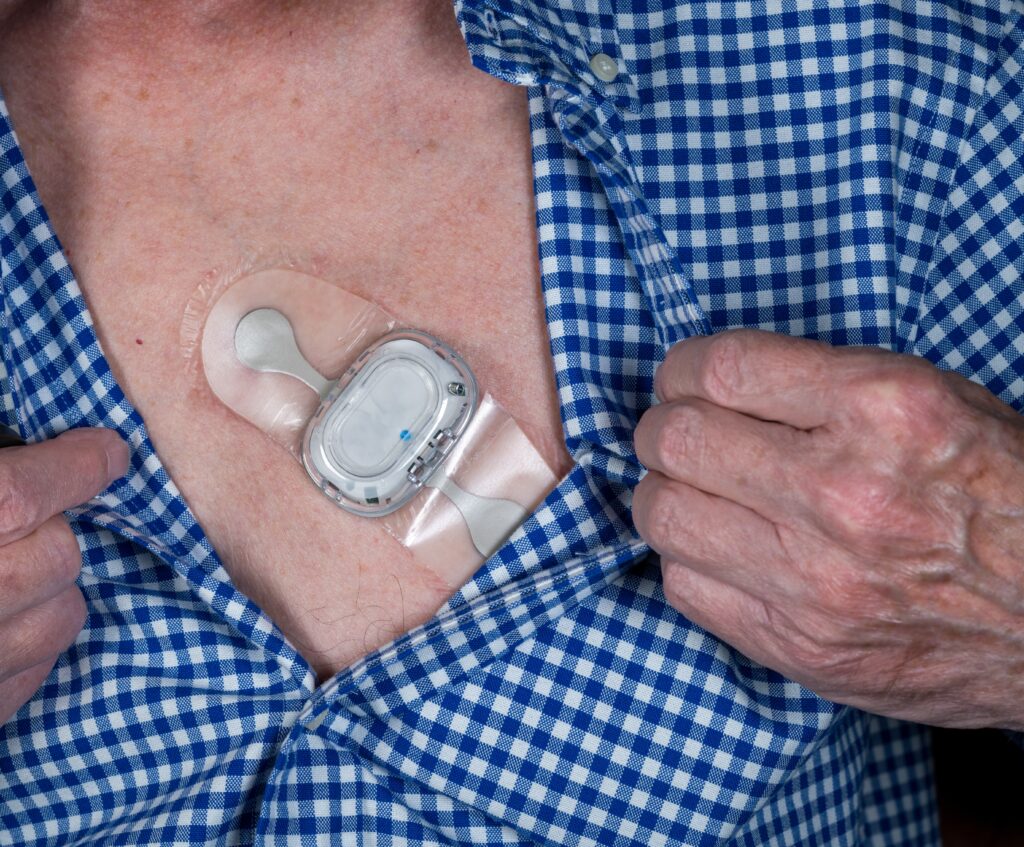
You likely have experienced a medical event, whether it was your routine doctor visit or a medical emergency. Yet the unsung heroes are the often-overlooked materials and devices that are used to alert, identify, fix, secure, manage or prevent future debilitating and expensive medical conditions. Medical adhesives and flexible materials are actually a critical component in modern healthcare. These versatile materials are used in various applications, from wearable tracking devices to wound care to cover patches for recovery, and have a profound impact on patient outcomes and medical practices.
At The Tape Lab, we understand the challenges with sourcing the right materials, including adhesives and flexible materials, that are both comfortable and safe. We believe creating the best product starts with having a basic understanding of those materials so you know what you are looking for when you create your breakthrough medical product.
With the goal to better understand adhesive materials, let’s explore the different types of medical adhesives, their applications, and the innovations driving their development.
The Basics of Medical Adhesives
Medical adhesives are specialized substances designed to bond biological tissues or medical devices to tissues. Unlike regular adhesives, medical-grade adhesives are formulated to be biocompatible, meaning they do not cause adverse reactions when in contact with living tissue. They must also be sterile and durable, ensuring they can withstand the body’s environment.
Types of Medical Adhesives
- Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs): These adhesives form a bond upon contact with the skin without needing heat or solvents. They are commonly used in wound dressings, bandages, and other sticky applications. PSAs are ideal for use on the skin due to their ability to adhere to various surfaces and their gentle removal, which minimizes damage to the skin.
- Cyanoacrylate Adhesives: Often referred to as “superglue,” cyanoacrylate adhesives are fast-drying and form a strong bond. In medical applications, they are used for wound closure, especially in emergency situations or for patients who cannot tolerate stitches. These adhesives create a protective barrier over the wound and help to speed up healing.
- Silicone Adhesives: Known for their flexibility and biocompatibility, silicone adhesives are used in applications requiring a high degree of elasticity, such as in ostomy devices or wearable sensors. They are gentle on the skin and less likely to cause allergic reactions, making them suitable for long-term use.
- Hydrocolloid Adhesives: These adhesives are used primarily in wound care. They consist of a gel-like substance that interacts with wound exudate to form a moist healing environment. Hydrocolloid adhesives are effective for treating chronic wounds and pressure ulcers.
- Bioadhesives: Bioadhesives are made from natural materials such as proteins and polysaccharides. They are designed to mimic natural tissue adhesion and are used in various surgical applications. Examples include fibrin glue, which helps in tissue repair and hemostasis, and chitosan-based adhesives, which have antimicrobial properties.
- Hydrogel Adhesives: Hydrogel is a water-rich, biocompatible substance designed to bond to skin or tissues while promoting healing and minimizing discomfort.
Applications in Healthcare
- Wound Care: Medical adhesive closure and dressings are crucial in managing and treating wounds. Adhesive bandages, hydrocolloid dressings, and adhesive strips help in protecting wounds, promoting healing, and reducing the risk of infection. Advanced wound care products use adhesives that maintain a moist environment, crucial for effective healing.
- Surgical Procedures: In surgery, adhesives are used for skin closure, internal tissue bonding, and securing medical devices. Surgical adhesives like cyanoacrylate and fibrin glue are employed to close incisions or seal internal tissues. They offer advantages over traditional sutures, such as reduced procedure time and minimal scarring.
- Device Securing: Adhesives play a significant role in securing medical devices such as catheters, electrodes, and ostomy appliances. They ensure that these devices remain in place, which is essential for accurate monitoring and effective treatment.
- Diagnostics and Monitoring: Wearable medical sensors and diagnostic patches rely on medical adhesives to stay attached to the skin. These adhesives need to be comfortable, secure, and capable of withstanding sweat and movement, making their role in wearable health technology critical.
Innovations and Future Trends
- Smart Adhesives: The integration of technology into medical adhesives is an exciting development. Smart adhesives can monitor physiological parameters and provide real-time data to healthcare providers. For instance, some smart adhesives can detect changes in wound conditions or patient vitals, enhancing personalized care.
- Bioresorbable Adhesives: Researchers are developing adhesives that gradually dissolve in the body over time. These bioresorbable adhesives are especially promising for internal use, reducing the need for additional procedures to remove them and minimizing potential complications.
- Antimicrobial Adhesives: To combat infections, new adhesives incorporate antimicrobial agents. These adhesives help reduce the risk of infection at the site of application, which is particularly important in wound care and surgical settings.
- Customized Adhesive Solutions: Advances in materials science are allowing for the development of highly specialized adhesives tailored to specific medical needs. This customization ensures optimal performance for different applications, whether it’s for delicate skin or challenging medical conditions.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their benefits, medical adhesives come with challenges that The Tape Lab experts understand and anticipate as they engineer any product. One significant issue is the potential for allergic reactions or skin irritation. Biocompatibility remains a critical concern, and ongoing research aims to minimize these risks. Additionally, the removal of adhesives, especially in sensitive areas, can cause discomfort or damage to the skin. Balancing adhesive strength with gentle removal is an ongoing area of development.
Medical adhesives are an indispensable part of modern medicine, providing essential support in wound care, surgical procedures, and device management. As technology advances, the field of medical adhesives continues to evolve, offering new solutions and improving patient care. From everyday bandages to sophisticated smart adhesives, these materials play a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of medical treatments and ensuring better outcomes for patients. As we move forward, innovations in medical adhesives will undoubtedly continue to shape the future of healthcare.
Get a Custom Medical Adhesive Created for Your New Product
At The Tape Lab, we’re not just creating high temperature adhesives; we’re crafting partnerships to bring your custom innovations to life. We design, manufacture, and transform adhesives for your personalized medical solution.
Already have an idea of what you need?
Want to pick the brain of an expert?
Contact The Tape Lab or request a quick quote, and let’s combine your vision with our knowledge and industry-leading capabilities to create a custom adhesive solution.